Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures for Gastrointestinal Health
Endoscopy is a minimally invasive medical procedure that allows doctors to examine the inside of the digestive tract using a flexible tube with a light and camera. These procedures play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating various gastrointestinal (GI) conditions. The primary types of endoscopy services include diagnostic and therapeutic gastroscopy, colonoscopy, enteroscopy, and capsule endoscopy.
1. Gastroscopy: Diagnosing and Treating Upper GI Disorders
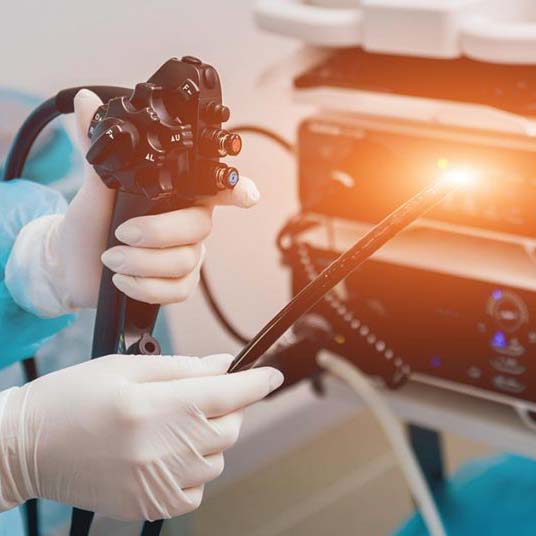
What is Gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy, also known as upper endoscopy, is a procedure used to examine the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). It is performed using an endoscope – a thin, flexible tube with a camera – inserted through the mouth and down the throat.
When is Gastroscopy Used?
Gastroscopy is used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, including:
- Diagnosing Conditions: It helps detect ulcers, gastritis, acid reflux (GERD), Barrett’s esophagus, celiac disease, esophageal or gastric varices, Helicobacter Pylori infection, cancer of the stomach or esophagus, and even pre-cancerous lesion/condition in the stomach or esophagus before they become cancer
- Investigating Symptoms: Patients experiencing chronic heartburn, difficulty swallowing, nausea, vomiting, unexplained weight loss, bloating, belching, or abdominal pain may require a gastroscopy. Intractable and unexplained chronic cough may sometimes be due to acid reflux which may need further investigation with gastroscopy.
- Therapeutic Applications: It is used for removing polyps, treating bleeding ulcers or varices, dilating strictures (narrowed areas), and removing foreign objects.
Gastroscopy is a quick outpatient procedure that typically takes about 15 minutes, with minimal recovery time. It can be done without sedation, or with moderate to deep sedation depending on patient’s preference.
2. Colonoscopy: A Crucial Tool for Colon Health
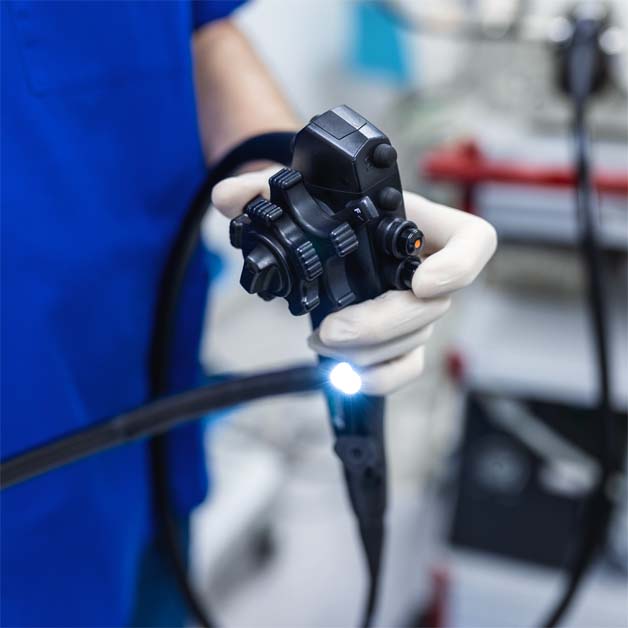
What is Colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is a procedure used to examine the large intestine (colon) and rectum. A long, flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the rectum to check for abnormalities.
When is Colonoscopy Used?
Colonoscopy is primarily performed for:
- Screening for Colorectal Cancer: It is recommended for individuals over 50 years old. The age for colon cancer screening may be younger than 50 years old for those with family history of colon cancer or Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
- Detecting and Removing Polyps: Precancerous growths (polyps) can be removed during the procedure to prevent colorectal cancer.
- Diagnosing GI Disorders: It helps identify conditions like Inflammatory Bowel Disease (ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease), diverticulosis, ulcers, piles (hemorrhoids) and infections.
- Investigating Symptoms: Patients experiencing rectal bleeding, chronic diarrhea, constipation, unexplained weight loss, or abdominal pain may need a colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy is highly effective in preventing colorectal cancer by detecting early-stage abnormalities. It can be done with moderate sedation, or with deep sedation depending on patient’s preference.
3. Enteroscopy: Examining the Small Intestine
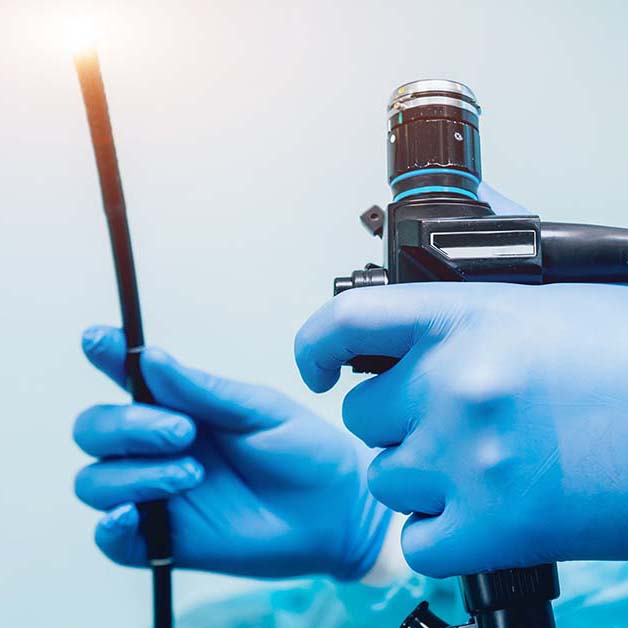
What is Enteroscopy?
Enteroscopy is a specialized endoscopic procedure that examines the small intestine, an area not accessible with gastroscopy or colonoscopy. It uses a longer endoscope with a balloon-assisted technique to navigate deeper into the intestine.
When is Enteroscopy Used?
This procedure is used to:
- Diagnose Small Bowel Disorders: It helps identify conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, ulcers, infections, and small bowel tumors.
- Detect and Treat Bleeding: It is capable of locating and stopping sources of GI bleeding.
Enteroscopy is often performed when capsule endoscopy detects abnormalities that require further examination. It is usually performed under deep sedation or general anaesthesia.
4. Capsule Endoscopy: A Non-Invasive Imaging Technique
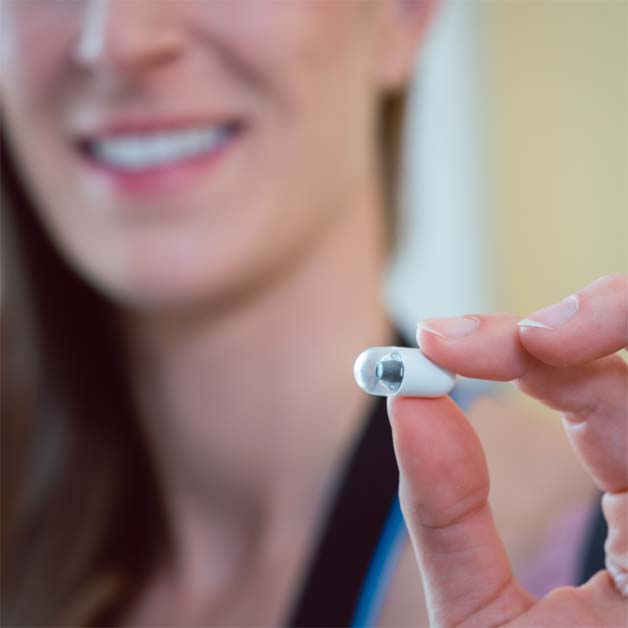

What is Capsule Endoscopy?
Capsule endoscopy is a cutting-edge diagnostic tool that involves swallowing a small, pill-sized camera. As the capsule travels through the digestive tract, it captures thousands of images, which are later reviewed by a specialist.
When is Capsule Endoscopy Used?
Capsule endoscopy is primarily used to:
- Detect Small Intestinal Disorders: It is particularly useful for diagnosing obscure GI bleeding, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and small bowel tumors.
- Identify Hidden Sources of Bleeding: It is often recommended when standard endoscopic tests fail to find the cause of anemia or bleeding.
- Monitor Disease Progression: Patients with conditions like Crohn’s disease may undergo capsule endoscopy to assess treatment effectiveness.
Since the capsule is disposable and passes naturally through the digestive system, this procedure is non-invasive and requires no sedation.
Get in touch with us today for expert gastroenterology and liver care.
Juanda Leo Gastroenterology and Liver Clinic© 2025 · All rights reserved · Powered by E3